Know Tensors with PyTorch
In this Notebook, we'll learn about Tensors, PyTorch, and how to create a simple tensor functions with PyTorch.
Pytorch
PyTorch is an open source machine learning library, a scientific computing framework, based on the Torch library.
The torch package contains data structures and a wide range of algorithms for deep learning for multi-dimensional tensors and mathematical operations over these are defined. And The fundamental unit in PyTorch is the Tensor.
Tensors
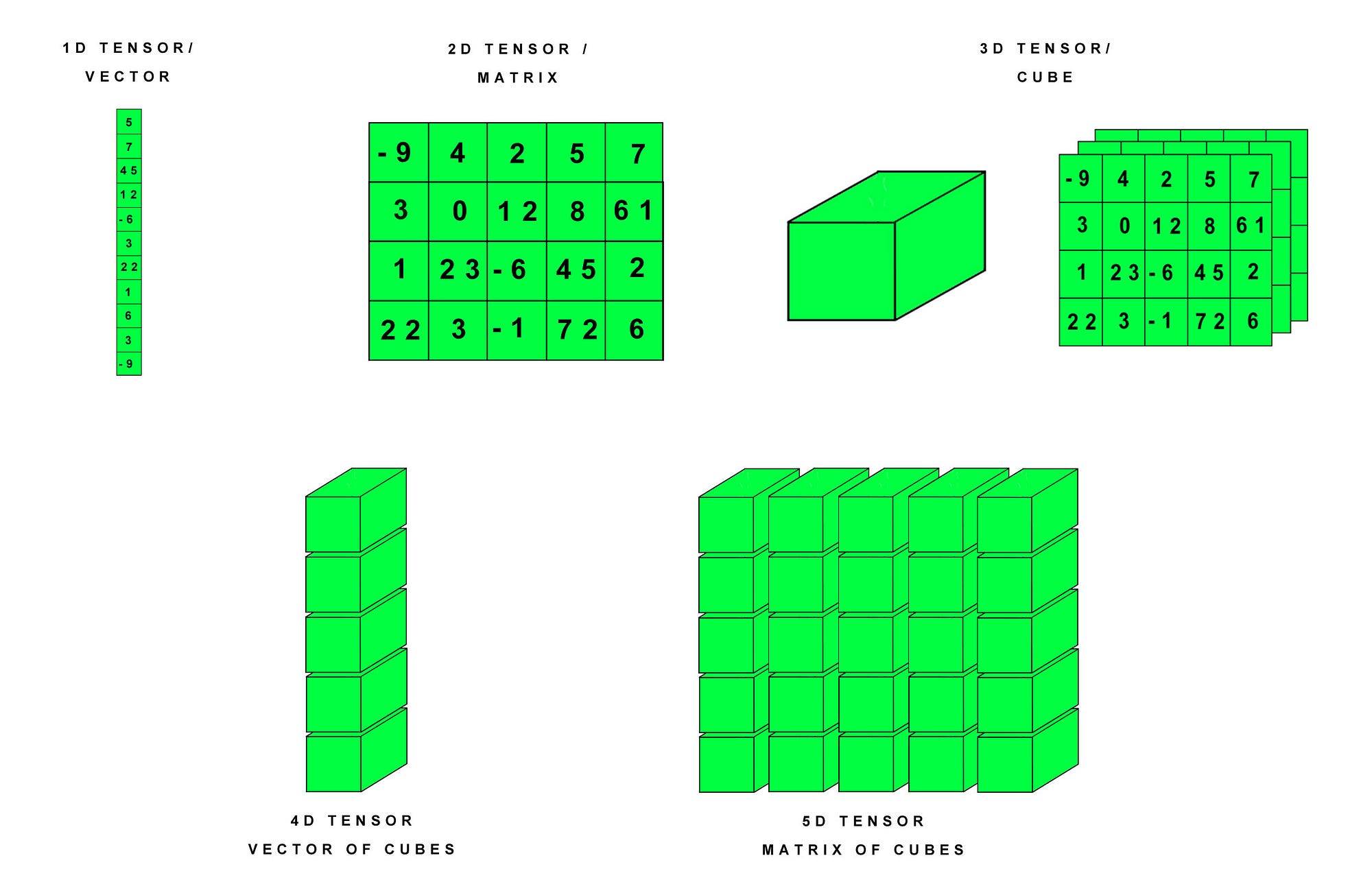
The concept of a tensor is a mathematical generalization of other more specific concepts. Some specific instances of tensors are.
- number
- scalar
- array
- vector
- 2d-array
- matrix
In other words, Tensors can take several different forms – for example: scalars and vectors (which are the simplest tensors), dual vectors, multi-linear maps between vector spaces, and even some operations such as the dot product.And it act as a Data Structure for Deep Learning.
Let's know insight about the following 5 tensor functions:
-
torch.tensor -
torch.cat -
torch.reshape -
torch.unbind -
torch.clamp
# Uncomment the command below if Numpy or PyTorch is not installed
!conda install numpy pytorch cpuonly -c pytorch -y
import torchCollecting package metadata (current_repodata.json): done
Solving environment: done
==> WARNING: A newer version of conda exists. <==
current version: 4.8.2
latest version: 4.8.3
Please update conda by running
$ conda update -n base conda
## Package Plan ##
environment location: /srv/conda/envs/notebook
added / updated specs:
- cpuonly
- numpy
- pytorch
The following packages will be downloaded:
package | build
---------------------------|-----------------
blas-2.15 | mkl 10 KB conda-forge
ca-certificates-2020.4.5.1 | hecc5488_0 146 KB conda-forge
certifi-2020.4.5.1 | py37hc8dfbb8_0 151 KB conda-forge
cpuonly-1.0 | 0 2 KB pytorch
intel-openmp-2020.1 | 217 780 KB defaults
libblas-3.8.0 | 15_mkl 10 KB conda-forge
libcblas-3.8.0 | 15_mkl 10 KB conda-forge
libgfortran-ng-7.5.0 | hdf63c60_6 1.7 MB conda-forge
liblapack-3.8.0 | 15_mkl 10 KB conda-forge
liblapacke-3.8.0 | 15_mkl 10 KB conda-forge
mkl-2020.1 | 217 129.0 MB defaults
ninja-1.10.0 | hc9558a2_0 1.9 MB conda-forge
numpy-1.18.4 | py37h8960a57_0 5.2 MB conda-forge
openssl-1.1.1g | h516909a_0 2.1 MB conda-forge
python_abi-3.7 | 1_cp37m 4 KB conda-forge
pytorch-1.5.0 | py3.7_cpu_0 90.5 MB pytorch
------------------------------------------------------------
Total: 231.5 MB
The following NEW packages will be INSTALLED:
blas conda-forge/linux-64::blas-2.15-mkl
cpuonly pytorch/noarch::cpuonly-1.0-0
intel-openmp pkgs/main/linux-64::intel-openmp-2020.1-217
libblas conda-forge/linux-64::libblas-3.8.0-15_mkl
libcblas conda-forge/linux-64::libcblas-3.8.0-15_mkl
libgfortran-ng conda-forge/linux-64::libgfortran-ng-7.5.0-hdf63c60_6
liblapack conda-forge/linux-64::liblapack-3.8.0-15_mkl
liblapacke conda-forge/linux-64::liblapacke-3.8.0-15_mkl
mkl pkgs/main/linux-64::mkl-2020.1-217
ninja conda-forge/linux-64::ninja-1.10.0-hc9558a2_0
numpy conda-forge/linux-64::numpy-1.18.4-py37h8960a57_0
python_abi conda-forge/linux-64::python_abi-3.7-1_cp37m
pytorch pytorch/linux-64::pytorch-1.5.0-py3.7_cpu_0
The following packages will be UPDATED:
ca-certificates 2019.11.28-hecc5488_0 --> 2020.4.5.1-hecc5488_0
certifi 2019.11.28-py37_0 --> 2020.4.5.1-py37hc8dfbb8_0
openssl 1.1.1d-h516909a_0 --> 1.1.1g-h516909a_0
Downloading and Extracting Packages
ninja-1.10.0 | 1.9 MB | ##################################### | 100%
pytorch-1.5.0 | 90.5 MB | ##################################### | 100%
liblapacke-3.8.0 | 10 KB | ##################################### | 100%
python_abi-3.7 | 4 KB | ##################################### | 100%
ca-certificates-2020 | 146 KB | ##################################### | 100%
blas-2.15 | 10 KB | ##################################### | 100%
libcblas-3.8.0 | 10 KB | ##################################### | 100%
numpy-1.18.4 | 5.2 MB | ##################################### | 100%
intel-openmp-2020.1 | 780 KB | ##################################### | 100%
cpuonly-1.0 | 2 KB | ##################################### | 100%
openssl-1.1.1g | 2.1 MB | ##################################### | 100%
liblapack-3.8.0 | 10 KB | ##################################### | 100%
certifi-2020.4.5.1 | 151 KB | ##################################### | 100%
libblas-3.8.0 | 10 KB | ##################################### | 100%
mkl-2020.1 | 129.0 MB | ##################################### | 100%
libgfortran-ng-7.5.0 | 1.7 MB | ##################################### | 100%
Preparing transaction: done
Verifying transaction: done
Executing transaction: done
Function 1 : How to create Pytorch Tensor
torch.tensor(data, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False) → Tensor
Constructs a tensor with data.
Parameters
-
data (array_like) – Initial data for the tensor. Can be a list, tuple, NumPy ndarray, scalar, and other types.
-
dtype (torch.dtype, optional) – the desired data type of returned tensor. Default: if None, infers data type from data.
-
device (torch.device, optional) – the desired device of returned tensor. (CPU TENSOR OR GPU TENSOR)
Default: if None, uses the current device for the default tensor type (see torch.set_default_tensor_type()). device will be the CPU for CPU tensor types and the current CUDA device for CUDA tensor types. -
requires_grad (bool, optional) – If autograd should record operations on the returned tensor. Default: False.
Note on: Autograd: Automatic Differentiation
The autograd package provides automatic differentiation for all operations on Tensors. It is a define-by-run framework, which means that your backprop is defined by how your code is run, and that every single iteration can be different.
torch.tensor is the central class of the package. If you set its attribute .requires_grad as True, it starts to track all operations on it. When you finish your computation you can call .backward() and have all the gradients computed automatically. The gradient for this tensor will be accumulated into .grad attribute.
- pin_memory (bool, optional) – If set, returned tensor would be allocated in the pinned memory. Works only for CPU tensors. Default: False.
Example-1.1
Lets create simple 1D-tensor and check out its data type
torch.tensor([1, 2, 3, 4]) # 1-D tensor using 1d array data
tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])